
Working group Ecology of benthic organisms - Running Projects
STATUS of the functions of biogenic reefs in the Baltic Sea with a focus on carbon fixation
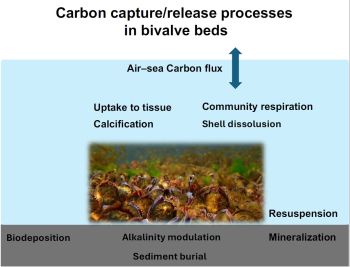
The STATUS project is dedicated to understanding and quantifying the carbon sequestration potential of biogenic reefs, particularly mussel beds, in the Baltic Sea. Led by the Benthology group at the Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research, Warnemünde (IOW), and funded by the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN), the project collaborates closely with the ArKoBi project (focusing on Arctica islandica in the Baltic Sea) and the DEFINE II project of the Alfred Wegener Institute (Bremerhaven), which explores similar themes in the North Sea.
The STATUS project follows a multi-phase workflow. Launched on October 1, 2024, the first year focuses on establishing a foundational understanding of carbon capture, storage, and release processes within Mytilus mussel beds. This phase involves compiling existing data on mussel bed distribution and biomass, paired with a gap analysis to inform subsequent field and experimental research.
In the following phases, STATUS will conduct targeted field and laboratory mesocosm experiments to measure specific carbon fluxes, including biodeposition, sediment carbon burial, and calcification. Using benthic flux measurements and sediment core analyses, the project aims to build a comprehensive carbon budget for mussel beds. Experimental data will support the development of predictive models to simulate how mussel bed ecosystems respond to varying environmental conditions, providing insights into their potential role in climate change mitigation.
STATUS aims to deliver actionable insights for policymakers and marine managers, highlighting the potential of mussel beds as a nature-based solution for carbon sequestration. By contributing to blue carbon strategies, the project seeks to support sustainable management practices that enhance biodiversity and ecological resilience in the Baltic Sea. Through these efforts, STATUS aspires to integrate mussel bed conservation into broader marine protection and climate mitigation initiatives.
Duration: 2024 - 2027
Investigation of the contribution of Arctica islandica to the carbon storage and biodiversity in the Baltic Sea (ArKoBi)

The project ArKoBi is investigating the extent to which the black quahog Arctica islandica and its associated biotopes play a role as a carbon sink (i.e. blue carbon) and how climate change and anthropogenic uses affect their biodiversity, reproduction and population structure and the associated carbon storage capacity. This is not only relevant in terms of species and biotope protection, but is also intended to contribute to federal policy goals for the conservation of biodiversity and climate protection. ArKoBi is working on three main topics: 1) The ecological function of A. islandica and its associated communities as a carbon sink or possibly also a carbon source at the organism and community level, 2) The population and reproduction dynamics of A. islandica in the Baltic Sea, especially in the nature reserve "Fehmarnbelt", their development with increasing environmental changes and anthropogenic uses as well as the consequences on the carbon storage capacity of the habitats, 3) The question whether A. islandica from the North Sea and the Baltic Sea represent genetically different populations and whether the Baltic Sea population reproduces independently. The ArKoBi project combines basic research with marine nature conservation and determines the potential for a further blue carbon ecosystem in the Baltic Sea. The findings can be used to derive possible conservation measures to protect the A. islandica-associated biotopes for both the climate and the environment.
Duration: 2023 - 2026
Assessment of habitats on the basis of macrozoobenthos along the salinity gradient in the southern Baltic according to the regulations of the Water Framework Directive (WFD) and the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) (2007-ongoing)
Internal project
- Sensitivity/tolerance of macrozoobenthos species in the southern Baltic (ES500.05-Werte)
Macrozoobenthos off South-West Africa (2004-ongoing)
In South West Africa the continental shelf near the mouth of the river Cunene represents a unique environment. Freshwater and sediment plumes reach the ocean just where the northward-flowing cold, nutrient-rich Benguela Current (the eastern boundary current of the South Atlantic subtropical gyre) digresses from the Namibian coast and meets the southward-flowing warm, nutrient-poor Angola Current (the southeast branch of the South Equatorial Countercurrent) forming a convergence zone at approximately 14-16°S known as Angola-Benguela Frontal Zone (ABFZ). The South West African shelf is also part of the “Benguela Current Large Marine Ecosystem” (BCLME), one of the four largest upwelling systems and one of the most productive areas on this planet. Upwelling stimulates primary and secondary production in the euphotic zone, which further promotes hypoxic areas in deeper strata. On the Namibian shelf, oxygen minimum zones occur even at depths of 30 m.
Macrozoobenthos was collected in 2004/2008/2011 on the shelf off Angola and Namibia. The taxonomical treatment led to descriptions of several new species among different groups. 13 new species and one new genus have been described in several scientific journals. The morphology and distribution of Ophiuroidea and Cumacea was examined in more detail.
Internal project; Analyses of the expeditions in 2004, 2008 and 2011
Benthos monitoring Baltic Sea (1992-ongoing)
Funding agreement: Federal Maritime and Hydrographic Agency (BSH)
==> Final monitoring report for 2007
Science Partnerships for the Assessment of Complex Earth System Processes - SPACES: Groundwater/Seawater Interaction along the South African South Coast and its Effects on Sustainable Coastal and Water Resource Management (2013-2016)
Funding Agreement: Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF)
Mapping and registration of marine habitats in the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) respectively (Cluster 6) (2012-2014)
For the implementation of environmental policies such as the European Marine Framework Directive in the German Baltic Sea and the North Sea, a profound knowledge on habitats and their distribution is required. Cluster 6 aims at a habitat classification for marine regions in the German waters based on empiric data.
Within this project, a complete habitat map of the marine protected areas in the German EEZ was designed and protected marine habitats according to §30 BNatSchG were mapped in the whole EEZ of the German Baltic Sea and the North Sea
Funding agreement: Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, BfN
Monitoring and assessment of benthos, habitats and alien species (Cluster 4, Benthos monitoring) (2011-2014)
Biotopes and habitats are in the focus of relevant European directives (NATURA 2000, Marine Strategy Framework Directive), regional conventions (e.g. OSPAR, HELCOM) and the federal law on nature protection to maintain the natural biodiversity and a good environmental status of the seas. This project in cooperation with the AWI was meant to improve the initiation and establishment of a monitoring program considering these guidelines in the North and Baltic Sea. The development of a monitoring concept and simultaneously the practical implementation by sampling and assessment were the main goals of this study. Mostly sedentary and stationary organisms as macrozoobenthos and macrophytes with highly sensitive reactions to the changing environment (anthropogenically and naturally) are significant indicators on a local, regional and more global scale.
Funding agreement: Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, BfN
Amphipoda project (2011-2013)
Internal project; Compilation of species characteristics in terms of a determination key (Baltic and its river watersheds)
Fehmarnbelt project - Benthic Fauna (2008-2011)
Femern A/S (part of Sund and Bælt Holding A/S, which is 100 percent owned by the Danish Transport Ministry.) is designing and planning a fixed link between Denmark and Germany across the Fehmarnbelt in the Belt Sea of the western Baltic Sea. One important part of this work is to prepare an Environmental Impact Assessment Statement (in Denmark a VVM; and in Germany a UVS) in order to get approval of the project by the national authorities in the two countries involved. The approval documents are based on technical background studies describing the environment of the area which may be impacted by the project (baseline descriptions) and assessing the expected impacts (impact assessment).
The main objective of the baseline study (2009 to 2010) was to establish a well-founded description of the benthic macrofauna in the Fehmarnbelt, the sea strait between the German island of Fehmarn and the Danish island of Lolland. The study covered the potential alignment area of the proposed fixed link and adjacent waters, based on extensive data acquisition and including biological parameters like abundance, biomass, species diversity and community structure. The Benthic Fauna Baseline Report describes the results of two years of extensive monitoring and mapping of the benthic fauna. Benthic epi- and infauna was sampled at 325 stations, with locations as shown in the figure using standardized methods (van Veen grabs operated from a ship at deep stations and frame samples operated by divers at shallower waters).
Funding agreement: Danish Hydrographic Institute (DHI)/Fehmarnbelt-Konstortium
Benthos monitoring North Sea (2008-2011)
Funding agreement: Federal Maritime and Hydrographic Agency (BSH)
Benthic monitoring of NATURA 2000 areas in the German Baltic (2009)
Funding agreement: Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, BfN
Field studies investigating possible impacts of offshore wind parks on the surrounding benthos ecology conducted on research platforms in the Baltic and North Sea (BeoFINO 2) (2005-2007)
Benthologic studies for the ecological assessment of potential windmill areas and mapping of NATURA 2000 areas in the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of the Baltic (2002-2006)
Funding agreement: Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, BfN
Accompanying ecological research on the use of offshore wind parks conducted on research platforms in the Baltic and North Sea (BeoFINO 1) (2001-2004)
WP 3: Effects of electromagnetic fields on marine organisms
Funding agreement: Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, BMU
Accompanying ecological research on the use of offshore wind parks conducted on research platforms in the Baltic and North Sea (BeoFINO 1) (2001-2004)
WP 2: Processes in the near range of the piles Baltic
Funding agreement: Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety, BMU
Inventory and mapping of Baltic Sea areas sensitive for oil spills (2002)
Funding agreement: Special Branch of the coastal states to combat marine pollution, SLM
Macrozoobenthos database (2001-2002)
Funding agreement: Federal Institute for Hydrology, BfG